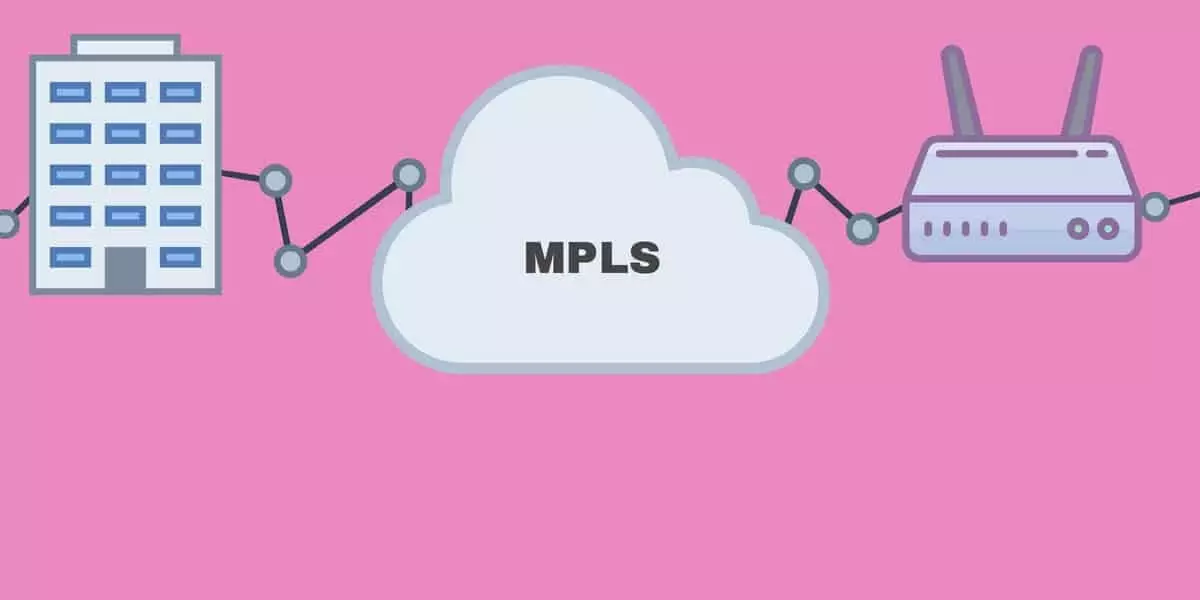
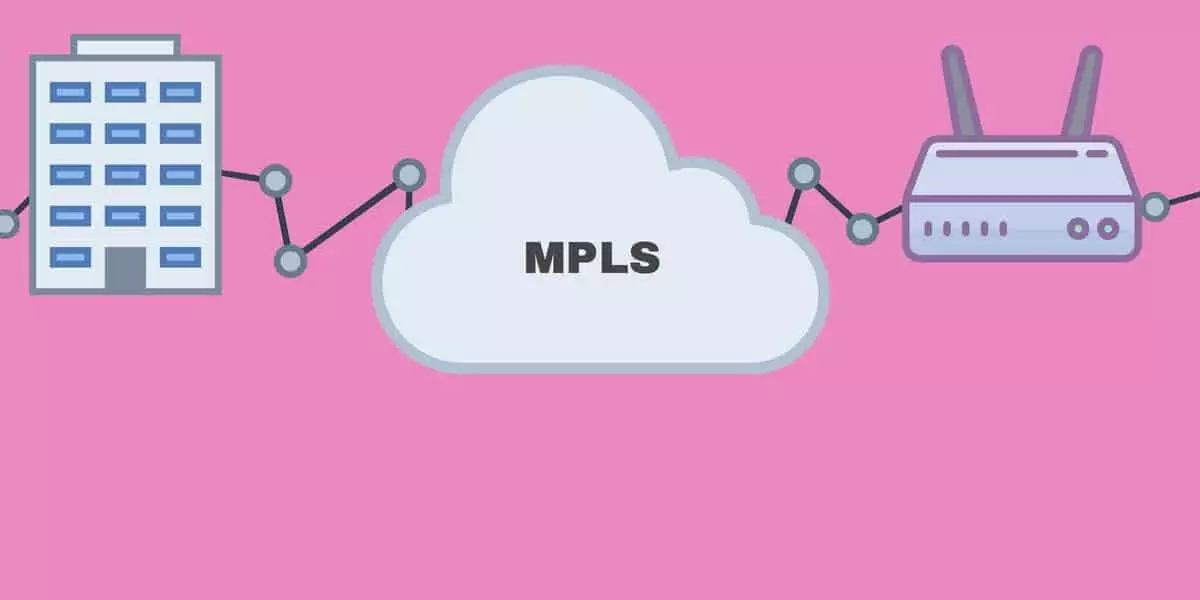
MPLS, or MultiProtocol Label Switching, is a mechanism to speed up and shape traffic flows across a network. MPLS works by tagging the traffic entering the MPLS network. When a router receives tagged traffic, it forwards it to the appropriate destination using pre-established labels.
MPLS (MultiProtocol Label Switching) has evolved into a de facto standard for fast-packet forwarding across an IP network. It is an IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standards-approved technology that’s designed to speed up the flow of traffic through a network and reduce congestion.
Traditional IP routing uses a complicated process to forward packets. This process determines the destination address of each packet so it can be sent to the correct destination. Routers store the destination information in their routing tables, and they use this information to determine where packets need to go next. The process of forwarding packets is time-consuming and complex, which can cause bottlenecks that slow down network traffic.
See Also: MPLS Explained In 5 Simple Steps
MPLS works by creating special labels for each packet as it enters the network. Each label contains routing information that enables switches to forward packets based on the label, rather than having to look up a packet’s IP address in its routing table. The label also identifies a path through which the packet should travel to reach its destination. MPLS prioritizes different types of data, such as voice and video, so that time-sensitive data gets priority over other types of data in the network queue.
MPLS is a high-performance network technique that directs data efficiently using labels instead of long addresses. Businesses seeking exposure in tech can advertise with us to reach professionals exploring advanced networking solutions like MPLS and its practical applications.
It consists of three components:
Label Switching Routers (LSR): These are the routers in the network that forward the packets based on the labels.
Forward Equivalence Class (FEC): These are set of IP packets that can be forwarded with the same treatment by the MPLS network, e.g., Packets belonging to a particular layer 4 protocol or coming from a particular source-destination pair.
LSP (Label Switched Path): Label Switched Path is nothing but a path between two LSRs with the same FEC values.

Frank Partnoy is a tech blogger who loves to share his thoughts about the latest gadgets and technology. He loves everything from smartphones, laptops, tablets and more!